



Agricultural-Municipal Gasification
Let’s process waste while protecting the environment in an economical and productive way.






and Financial Projections




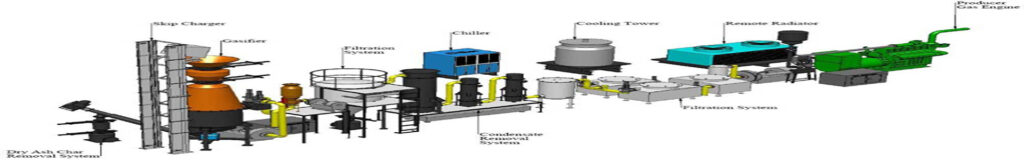
Transportation and Installation


Getting Started

You protect the environment
Generate Profits


MAKING THE DIFFERENCE
The generation of waste and its processing is one of the main challenges facing the human race.
As we urbanize, the amount of waste we are generating, per capita, continues to increase. But there are very few technologies that can process this waste in a sustainable way.
Ankur Scientific has, over the past few years, been dedicated to finding solutions for waste such as MSW, EFB, poultry house waste, etc. The idea has basically been to work on technologies that can process the waste, without harmful emissions, producing energy (which allows the projects to be cost effective / sustainable) and at scales that allow the waste to be processed in a distributed manner.
Gasification is one of the best solutions for handling these wastes. However, the process is complex and requires a huge development effort and innovative ideas to successfully process the widely varying wastes. Once successfully developed, the process is unique in that it transforms the usable carbon and hydrogen compound of the waste into a gas called producer gas, leaving almost all of the undesirable components in solid form, along with some percentage of fixed carbon. This ensures that the waste is effectively disposed of while recovering energy.
The Process
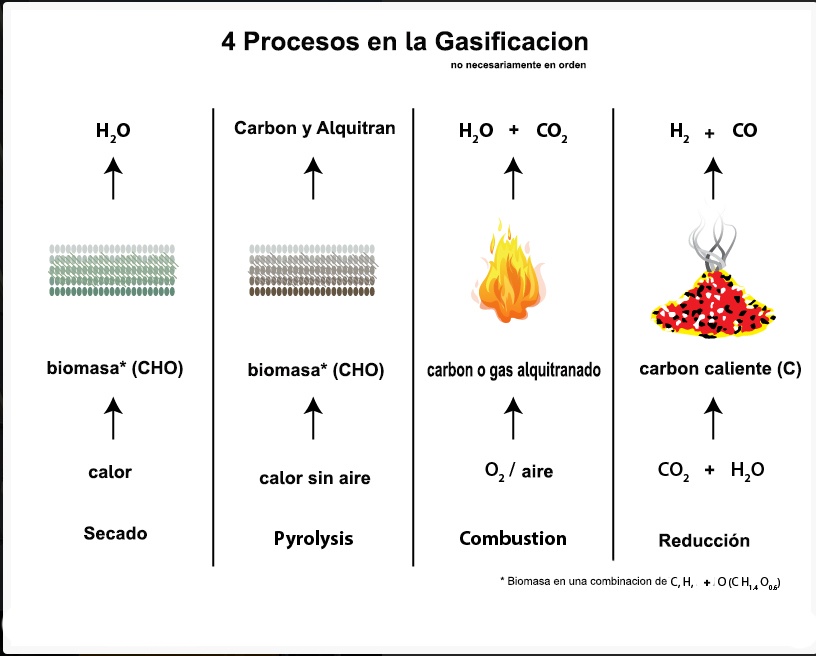
Gasification is the conversion of solid hydrocarbon wastes (wood/wood waste, agricultural waste, chicken manure, coal, municipal waste, etc.) into a combustible gas mixture called Producer Gas / SynGas. The gasifier is essentially a chemical reactor where several physical and chemical processes take place and decompose the solid fuel into producer gases. Four distinct processes take place in a gasifier:
1. fuel drying The moisture in the feed exits in this zone in the form of water vapor. Drying takes place at the top of the gasifier, through heat transferred from the high temperature combustion zone.
2. Pyrolysis This is the chemical decomposition of organic materials by heating in the absence of oxygen at temperatures above 200 degrees C. During pyrolysis, volatiles (in the form of gas) are released and char is produced.
3. Combustion This is where controlled oxygen is administered to the fuel and oxidation/combustion occurs. Heat and energy are released.
4. Reduction The products of combustion mainly CO2 (carbon dioxide) and H2O (water vapor) are reduced in the presence of carbon at high temperature to eventually give CO (carbon monoxide) and H2 (hydrogen).
Important advantages
The process allows waste to be handled from the 100 kg per hour level up to the 10,000 kg per hour level. Therefore, this is the only technology that allows small configurations in small towns and cities, etc., which were not previously covered by waste-to-energy technologies. This also allows for decentralized waste processing even for large metropolises (instead of all waste having to be transported to a central landfill).
The process is highly efficient. This allows projects to be financially viable / the most cost-effective solution.
The gasification performed by Ankur Scientific ensures that no treated water is used throughout the process.
In conclusion, here we have a technology that not only handles waste in a way that generates a utility (in a distributed manner), but also does so in an environmentally friendly way, with very low emissions that are well below the permissible limits.
The solid waste generated is only ash + charcoal/charcoal, both of which are non-hazardous to the environment.Charcoal/charcoal is a mixture of fixed carbon with ash and has a high value for soil fertility and is recognized for its use in organic agriculture.Gasification is successful without problems in gaseous emissions. This is achieved in the following way:
Gasification is a process that converts solid fuels to gaseous fuel in an oxygen deficient environment. The process involves only partial combustion of solids and generates a small amount of ash and carbon. The ash and inert material responsible for particulate emissions are processed within the reduction/charcoal bed and, therefore, the gas generated by gasification has little ash and suspended particulate matter. Thus, the levels of SPM in the stack are extremely low.
Heavy metals such as Cd, Cr, Hg, Pb, Fe could be present in the waste. While most of these are retained in the ash, our gas conditioning system removes the volatile heavy metal chlorides formed during the gasification process. Therefore, there is no possibility of heavy metal contamination.
The sulfur-based organic compounds produced in our gasifiers have a significantly lower concentration and are removed by our gas conditioning systems. Thus, the gas generated as a final product is composed of negligible amounts of these elements, therefore, after combustion, the sulfur oxides formed are always lower than the limit permitted by all pollution control agencies.
The gas generated is also a low energy intensity gas. Therefore, when burned, there is little chance of forming NOx. Therefore, the gas generated has negligible amounts of NOx.
Systems for all Needs
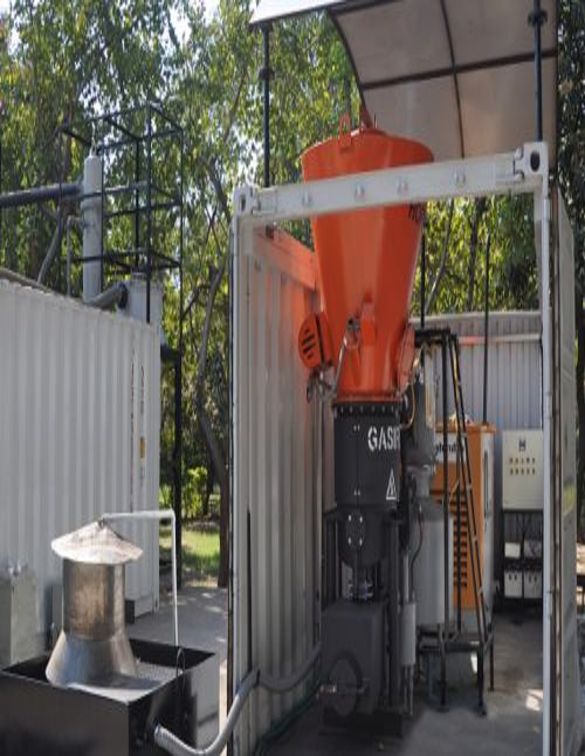
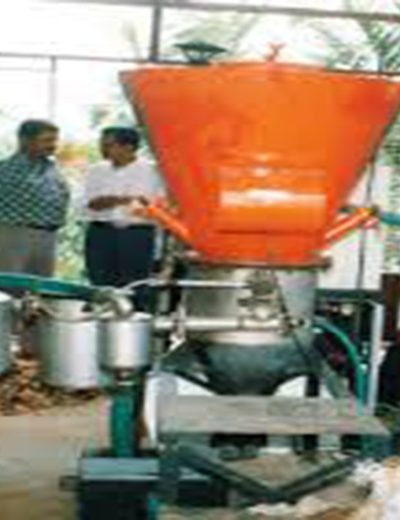





GASIFIERS FOR MANY TYPES OF WASTE AND QUANTITIES
An extensive line of equipment to handle from 10kg to 10,000kg per hour, with the possibility of handling several lines in parallel.
